Understand why using Frotcom to analyze costs and fuel consumption per distance and time gives you a more transparent and fairer view of fleet performance.
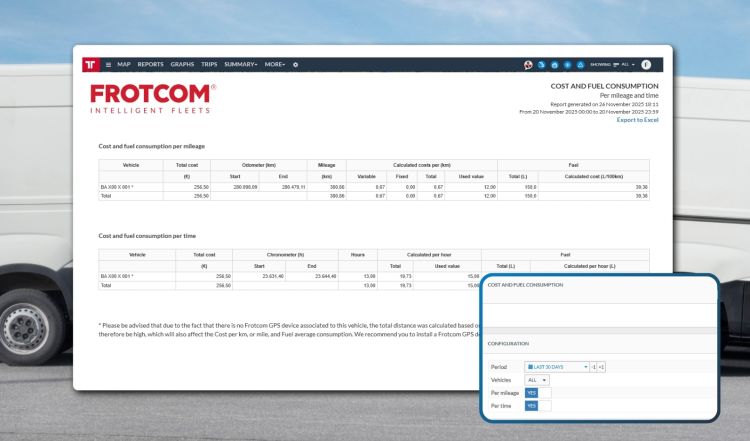
When fleets assess performance, totals often dominate the conversation; indicators such as total fuel spend, total mileage, or total operating cost can seem like reliable metrics at first glance. However, these figures rarely provide a comprehensive overview of your fleet's state. To understand how efficient your operation is, fleet costs and fuel consumption must be normalized and analyzed based on how assets are used, whether that usage is measured in distance or time.
Normalizing costs helps remove distortions caused by workload differences, operating environments, and duty cycles. It allows fleet managers to compare assets fairly, identify inefficiencies, and make decisions based on performance rather than assumptions.
Why Totals Can Be Misleading
Two assets may generate similar total fuel costs over a month, yet operate under very different conditions. One may travel longer distances at steady speeds, while another spends more time in traffic, idling, or operating in urban environments. Likewise, a machine may run for many hours while barely moving at all. Looking only at total consumption hides these differences and can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
By analyzing fuel consumption and costs per mile or per hour, you gain insights into how efficiently vehicles are being used, regardless of workload or distance covered.
Cost per Distance: The Right Metric for Vehicles
For road vehicles, usage is primarily based on distance. Cars, vans, and trucks are designed to transport goods or people from one point to another, making cost per kilometer/mile the most relevant and comparable metric.
Analyzing costs and fuel consumption per kilometer allows you to:
- Compare vehicles fairly, even when workloads differ;
- Identify improved routes or assignments that generate higher costs;
- Detect inefficient driving behavior;
- Support preventive maintenance and replacement decisions.
This normalized approach ensures that performance is measured, evaluated, and in line with how vehicles are actually used.
Cost per Hour: Essential for Machines and Low-Mileage Assets
Not all fleet assets are driven primarily by distance; for instance, machines used in construction, agriculture, or industrial environments often operate for long hours while covering very little mileage. In these cases, cost per hour is the correct metric.
For this type of equipment, the cost per kilometer/mile can be misleading or irrelevant. Instead, the cost per hour reflects actual usage, supporting an accurate analysis of fuel consumption, wear, and operating efficiency.
Using the correct metric empowers you to:
- Understand true operating costs.
- Plan maintenance more effectively.
- Compare similar machines fairly.
- Make informed investment and replacement decisions.
Turning Cost Data Into Practical Insight
With Frotcom, cost and fuel data can be analyzed in a centralized platform, allowing fleet managers to apply the appropriate metric to each type of asset. By relating costs to either distance or operating time, performance becomes easier to evaluate, explain, and improve across mixed fleets.
This contextual analysis supports objective decision-making, whether reviewing vehicle assignments, optimizing machine utilization, or evaluating the long-term impact of operational changes.
Intelligent Decisions with Better Metrics
Normalizing costs by distance or time is a fundamental step toward fair analysis and better management. When performance is measured using the right metric for each asset, it becomes easier to reduce waste, control costs, and improve overall fleet productivity. Frotcom helps you transform cost and fuel data into meaningful metrics that support efficient and different fleet activities.
Want a clearer view of your fleet's real performance? Discover how Frotcom can help you analyze costs and fuel consumption with the context you need to manage more effectively.
- Frotcom
- Fuel management
- Fleet cost management
- Fuel Consumption Analysis
- Fuel management
- Cost per Mile
- Cost per Hour
- Fleet performance metrics
- Fleet efficiency
- Telematics
- Operational Cost Control

